- Natural Resource Today Weekly
- Posts
- Natural Resource Today Weekly - Issue #29
Natural Resource Today Weekly - Issue #29
The most significant scientific findings you should know in less than 2 minutes.
Research News
The University of Edinburgh:
In a recent study published in the journal Annals of Neurology, researchers provide better understanding of the association between breast milk feeding and brain development in premature babies.
Read More:
Cornell University:
New research sheds light on the influence of sociability on competition among birds. The study is published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.
Read More:
University of KwaZulu-Natal:
Researchers provide new insights into subterranean ants of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. The study is published in the African Journal of Ecology.
Read More:
Cape Peninsula University of Technology:
In a study published in the journal Heliyon, researchers shed light on acid mine drainage remediation system.
Read More:
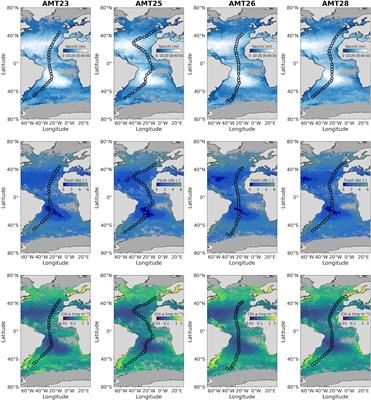
University of Exeter:
Researchers provide better understanding of techniques for monitoring phytoplankton biomass. The study is published in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science.
Read More:
University of California, Davis:
In a new study published in the journal Climate of the Past, researchers shed light on the Holocene climate of the Western United States.
Read More:
University of Tsukuba:
Researchers provide better understanding of the link between hippocampal volume and physical balance in healthy older people. The study is published in the journal Gait & Posture.
Read More:
University of Bristol:
In a new study published in the journal Nature, researchers provide new insights into carbon sink of recovering tropical forests in the Amazon, Borneo and Central Africa.
Read More:
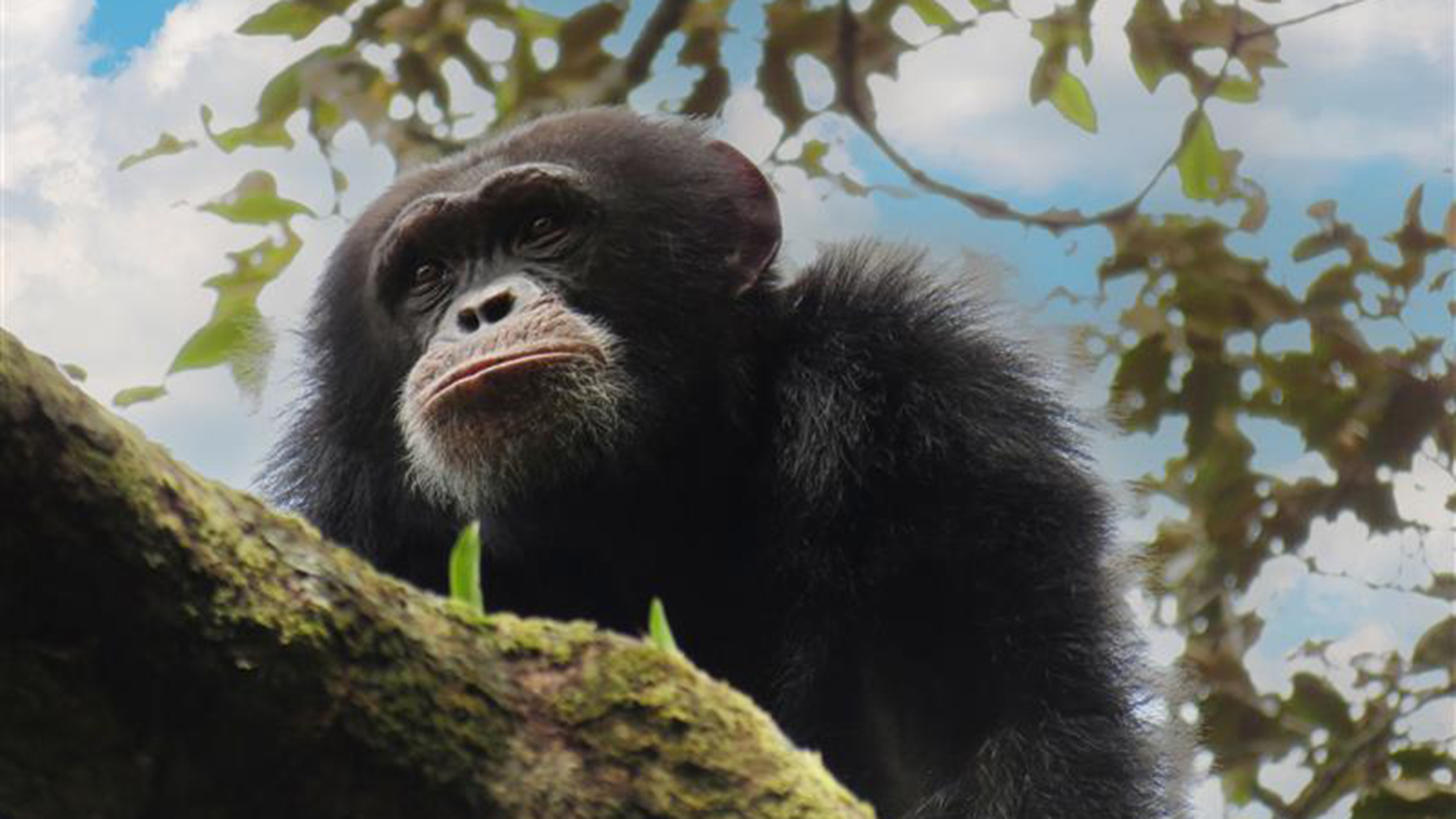
University of Zurich:
Researchers have used genetic analysis to estimate population structure of the western chimpanzees in the Nimba Mountains, Guinea. The study is published in the journal Conservation Science and Practice.
Read More:
University of California San Diego:
Researchers provide new insights into coral reef hypoxia. The study is published in the journal Nature Climate Change.
Read More: